Project Development Approaches
Code First#
You can work with two options in the Code First approach
Relational database
Document-oriented database
Relational database#
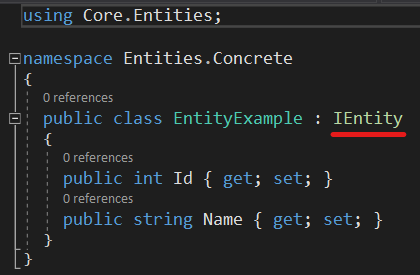
If a relational database (RDBMS) entity object is to be created in the Code First approach, it should be created under the Concrete folder in the Entities layer.
When a relational database will be used, the created class is expected to be implemented from the IEntity Interface. DevArchitecture Code Generator will understand that you want to work with a relational database and accordingly the code generator will generate the relevant methods and classes. Example class writing for relational database is presented as follows.
Document-Oriented Database (NoSQL)#
If a document-oriented database entity object is to be created in the Code First approach, it should be created under the Concrete folder in the Entities layer.
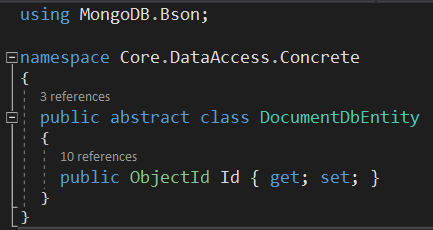
When using a document-oriented database, the created class is expected to inherit from the DocumentDbEntity abstract class. DevArchitecture Code Generator will understand that you want to work with a document-oriented database and accordingly the code generator will generate the relevant methods and classes.
It is not recommended to write a property representing the Primary Key used in relational databases in these classes. Within the DocumentDbEntity abstract class, the ObjectId key for MongoDB is inherited.
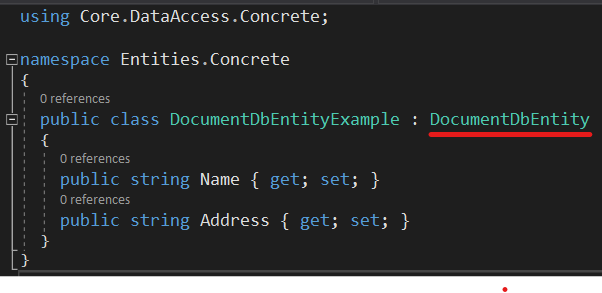
Example class writing for MongoDB is presented as follows.
Database First#
DevArchitecture Code Generator is used for the Database First approach.
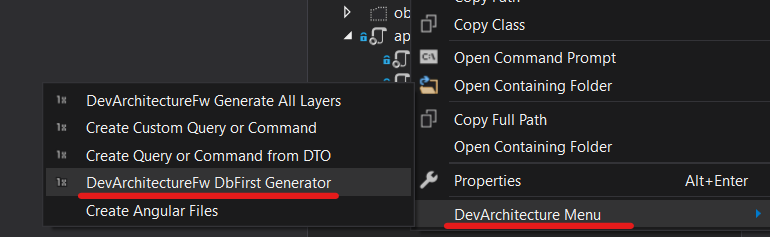
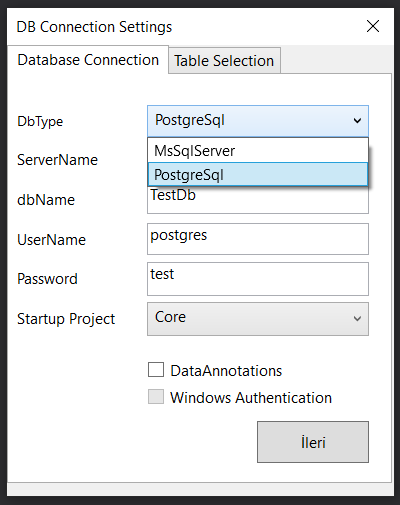
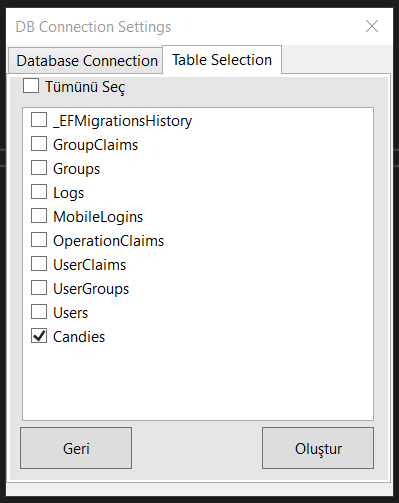
On the screen that opens, the database to be connected and the connection information are defined. It comes with Database First support for DevArchitecture MsSqlServer and PostgreSql. After selecting the connection information and Startup Project as WebAPI, the next button is pressed. Tables for which Database classes will be created are selected in the Table Selection tab. After that, click the Create button.
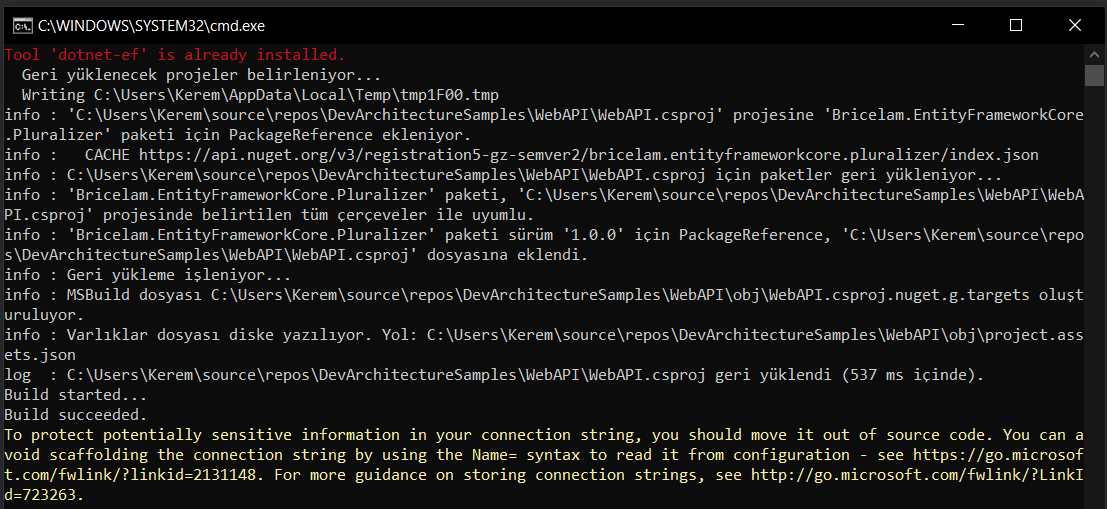
The Command Line screen below will automatically close. Database class is created under Entities\Conctere Folder and FakeDbContext class is created under DataAccess\Concrete\EntityFramework\Contexts folder. The FakeDbContext class is created temporarily for OnModelCreating only. If necessary, the relations formed here can be used by creating separate classes with the copy and paste method under DataAccess\Concrete\Configurations.
The database class resulting from this process should be as follows.
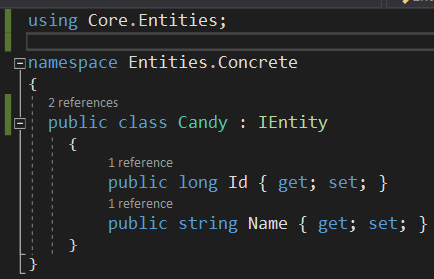
Right click on this class again. Click on DevArchitecture Generate All Layers.
Related methods and classes are created for all layers. In addition, all necessary configuration such as Autofac DI Registration operations, DbSet definitions for DbContext are defined by DevArchitecture Code Generator within the required classes and methods.
authors: Kerem VARIŞ, Veli GÖRGÜLÜ